APIs are the backbone of modern applications, and their stability under load directly impacts user experience. Without proper testing, high traffic can cause slowdowns, errors, or outages. API load testing tools help simulate real-world usage by sending concurrent requests, tracking response times, and exposing bottlenecks. In this guide, we’ll review the top API load testing tools for 2026, compare their features, and outline what to look for when selecting the right solution for your team.
Key Takeaways
- API load testing ensures reliability under heavy traffic.
- Look for scalability, protocol support, CI/CD integration, reporting, and ease of setup.
- Open-source tools (JMeter, k6, Locust) save costs but need more setup.
- Enterprise tools (PFLB, LoadRunner) provide cloud infra, advanced analytics, and support.
- Pricing varies: free OSS vs. usage-based cloud tiers.
What Is API Load Testing?
API load testing is the process of measuring how an API performs when it is hit with a high volume of requests at the same time. Instead of testing a single call in isolation, load testing simulates hundreds or thousands of concurrent users or applications interacting with the API. This helps teams identify slow endpoints, memory leaks, database bottlenecks, and other issues that may not appear under light traffic.
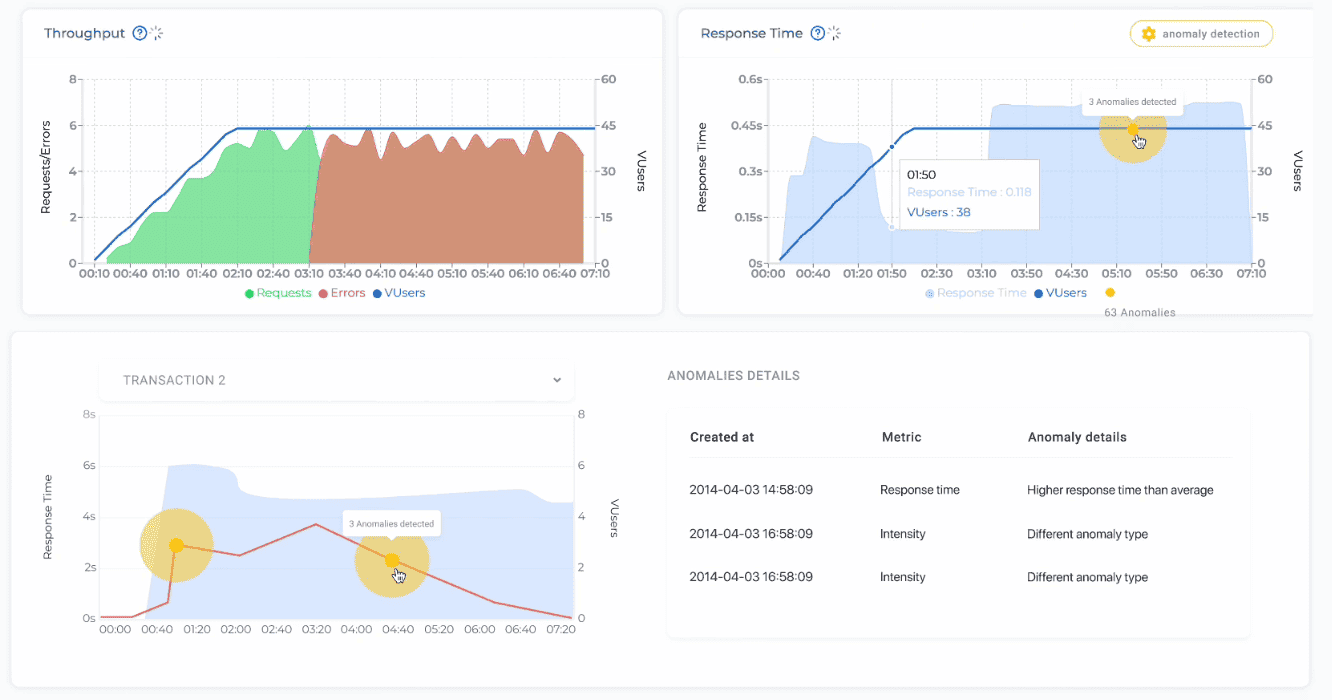
A good API load test tracks metrics such as response time, error rate, and throughput, and compares them against service-level objectives (SLOs). By running these tests before production launches, or continuously in CI/CD pipelines, organizations can ensure that APIs remain stable during real-world peaks in demand.
Best API Performance Testing Tools: Comparison Table
Key Features of Effective API Load Testing Tools
To choose the right API load testing tool you should focus on the features that directly affect performance and usability. Here are the most important ones to evaluate:
- Scalability — ability to simulate thousands or millions of concurrent requests without stability issues. Read also about IoT Testing.
- Protocol support — REST, GraphQL, SOAP, gRPC, and WebSockets should be covered for modern APIs.
- Reporting & analytics — real-time dashboards, trend tracking, and clear reports that pinpoint bottlenecks.
- Ease of setup — cloud-based load generators save time, while self-hosted tools may require significant configuration.
- Integrations — CI/CD tools like Jenkins or GitHub Actions, plus observability platforms such as Grafana, DataDog, or APM tools.
- Flexibility — scripting in Python, JavaScript, or DSL for developers, versus no-code builders for broader teams.
- Budget fit — open-source tools minimize cost but require effort; enterprise-grade platforms deliver advanced features and support at a higher price.
1. PFLB — Enterprise-Grade API Load Testing with AI Insights
PFLB is a professional load testing platform built to evaluate APIs and web applications at scale. Unlike open-source tools that require manual setup, PFLB provides pre-configured cloud infrastructure with distributed load generators across 20+ AWS regions, allowing teams to launch large-scale tests in minutes.
One of its standout features is AI-powered analysis. PFLB doesn’t just report response times and error rates; it highlights anomalies and helps pinpoint the root cause of performance bottlenecks. Combined with customizable dashboards in Grafana and full integration with Postman, this makes it easier for both engineers and managers to interpret results.
PFLB also integrates smoothly with common developer workflows. Teams can import request collections from Postman or Insomnia, reuse JMeter test plans, or build scenarios directly in its no-code interface. With CI/CD compatibility, tests can run automatically during deployments, ensuring reliability before each release.
Best for
Enterprises and scaling SaaS teams that need distributed API load testing with advanced analytics and minimal setup.
Pros
- Hosted load generators with global reach.
- AI-driven insights to detect bottlenecks faster.
- No-code test builder plus support for HAR, Postman, Insomnia, and JMeter imports.
- SLA/SLO tracking and custom reporting via Grafana.
- CI/CD and API integration for automated testing pipelines.
- Option to combine with expert consulting services.
Cons
- Free tier is limited in runs and virtual user hours.
- Lacks built-in APM integrations (e.g., New Relic, Dynatrace).
- No browser-based load testing.
Protocols supported
HTTP/HTTPS, REST, SOAP, gRPC, Kafka, MQ, plus full JMeter protocol coverage.
2. LoadRunner — Enterprise Legacy with Hybrid Flexibility
LoadRunner is one of the longest-standing performance testing tools, widely used in enterprises that require complex and large-scale test scenarios. Now offered by OpenText, it supports cloud, on-premise, and hybrid deployments, giving organizations flexibility in how they run tests. For API load testing, LoadRunner can simulate thousands of concurrent requests with precision and provide detailed analytics.
Its strength lies in robust scalability and the ability to model highly customized scenarios across different protocols. LoadRunner integrates with CI/CD tools such as Jenkins and Azure DevOps, enabling continuous performance validation. It also provides real-time dashboards and advanced reporting, which help QA and DevOps teams track throughput, latency, and error rates under heavy loads.
However, LoadRunner comes with trade-offs. It is resource-intensive, requires significant expertise to configure, and its pricing is among the highest in the market. This makes it less attractive for smaller teams or startups but a dependable choice for enterprises managing mission-critical systems.
Best for
Large organizations needing highly scalable, customizable performance testing across hybrid environments.
Pros
- Enterprise-grade scalability with precise control.
- Hybrid deployment: cloud, on-premise, or mixed models.
- Wide protocol support beyond APIs (web, mobile, databases).
- Deep integration with CI/CD pipelines.
- Advanced analytics and real-time reporting.
Cons
- High licensing and operating costs.
- Steep learning curve; setup requires expertise.
- Slower to adapt compared to newer, lightweight tools.
Protocols supported
REST, SOAP, HTTP/HTTPS, WebSockets, plus extensive enterprise protocol coverage (databases, messaging, legacy systems).
3. Gatling — High-Concurrency Testing with Developer Control
Gatling is an open-source load testing tool that appeals to developers who prefer scripting and automation. Scenarios are written in Scala or Java, giving teams fine-grained control over API test logic. For organizations that want managed infrastructure, Gatling Enterprise offers hosted load generators, advanced reporting, and integrations with popular CI/CD platforms.
One of Gatling’s biggest advantages is its ability to scale to very high user loads at a competitive price point, especially in the Enterprise Cloud edition. Developers can also extend functionality with official and community plugins for messaging systems, databases, and more. Reports are generated automatically with detailed graphs, making it easier to analyze throughput, latency, and error patterns.
That said, Gatling has a steeper learning curve compared to tools with no-code builders. Teams without Java/Scala experience may struggle initially, and the open-source edition requires self-hosted infrastructure. Reporting is functional but less advanced than the observability-rich dashboards offered by tools like PFLB or K6.
Best for
Developer-driven teams that want a script-based load testing solution with strong scalability.
Pros
- Open-source edition is free and highly flexible.
- Gatling Enterprise adds hosted load generators and reporting.
- Strong scalability: supports very high concurrency levels.
- Plugins available for Kafka, RabbitMQ, JDBC, and more.
- Integrates with Jenkins, GitLab, and other CI/CD tools.
Cons
- Requires knowledge of Scala or Java.
- Self-hosted infra needed for the free version.
- Smaller community compared to JMeter.
- Analytics less advanced than modern observability-focused tools.
Protocols supported
HTTP/HTTPS, REST, WebSocket, JMS, SOAP, MQTT, HTTP/2, JDBC.
4. k6 — Developer-Friendly Load Testing with Observability
K6 is an open-source load testing tool designed with developers in mind. Tests are scripted in JavaScript, making it accessible for teams already comfortable with web development. For larger-scale projects, Grafana Cloud k6 adds hosted load generators, distributed execution from 20+ global regions, and direct integration with the Grafana observability stack.
The biggest strength of k6 is its tight link to monitoring and observability. Performance test results can be correlated with metrics, logs, and traces in Grafana, giving DevOps teams end-to-end visibility. SLO-based pass/fail thresholds help enforce reliability standards in CI/CD pipelines, and real-time dashboards make test outcomes easy to interpret.
On the flip side, k6 can feel developer-centric. Non-technical users may struggle with scripting, and while the tool supports key modern protocols like gRPC and GraphQL, it does not natively handle JMeter or Gatling scripts. Pricing for the cloud version can also be confusing, as costs are tied not only to virtual user hours but also to metrics storage and visualization.
Best for
Developer and SRE teams that want a lightweight, scriptable API load testing tool with strong observability integration.
Pros
- JavaScript-based scripting is approachable for web developers.
- Grafana Cloud k6 provides global hosted load generators.
- Real-time dashboards with direct Grafana integration.
- SLO-based thresholds for automated pass/fail criteria.
- Strong support for REST, gRPC, and GraphQL.
Cons
- Requires coding; not suited for no-code testers.
- No support for JMeter or Gatling script reuse.
- Cloud pricing model can be difficult to estimate.
- Occasional instability with long-running WebSocket tests.
Protocols supported
HTTP/HTTPS, REST, WebSocket, gRPC, GraphQL, Kafka (via extension), browser-based testing (via xk6-browser).
5. JMeter — Open-Source Standard for API Load Testing
Apache JMeter is one of the most widely used open-source load testing tools. Originally designed for web applications, it has grown into a flexible platform capable of testing APIs, databases, messaging systems, and more. Its biggest advantage is its extensive plugin ecosystem, which allows teams to extend functionality and adapt it to almost any scenario.
JMeter supports distributed testing, meaning multiple machines can be used to generate high loads. With plugins for CI/CD tools and integrations with third-party dashboards like Grafana, JMeter can be scaled into enterprise workflows. However, the setup is manual — teams must manage infrastructure, configure load generators, and optimize test environments themselves.
Read also: JMeter Parameterization Guide
While free, JMeter comes with trade-offs. The learning curve can be steep, especially for beginners. Reporting is basic unless paired with external tools, and the interface feels outdated compared to newer cloud platforms. Still, it remains the default choice for many teams thanks to its flexibility, community support, and zero licensing cost.
Best for
Teams with technical expertise that want a free, highly customizable load testing solution.
Pros
- Free and open-source
- Huge plugin ecosystem and strong community support.
- Supports a wide range of protocols beyond REST.
- Flexible scripting and configuration options.
- Can integrate with Grafana and CI/CD pipelines.
Cons
- Steep learning curve for new users.
- Requires manual infrastructure setup.
- Outdated UI and limited built-in reporting.
- Performance issues possible at very high loads without tuning.
Protocols supported
HTTP/HTTPS, REST, SOAP, FTP, JDBC, JMS, LDAP, SMTP, TCP/UDP, and many more through plugins.
6. Artillery — Lightweight Load Testing for Modern APIs
Artillery is an open-source load testing tool built for developers who need flexibility without heavy setup. Tests are written in YAML or JavaScript, making it approachable for teams already familiar with scripting. For larger workloads, Artillery Pro and Artillery Cloud provide distributed execution, hosted load generators, and visual dashboards.
A key advantage of Artillery is its strong modern protocol support. It handles REST, WebSockets, GraphQL, gRPC, and Kafka, which makes it well-suited for testing microservices and event-driven architectures. It also supports browser-based testing with Playwright, allowing both API and front-end validation within the same tool.
The downside is that Artillery is developer-focused. There’s no no-code builder, and reports are less detailed than those offered by enterprise platforms. It also lacks compatibility with JMeter or Gatling scripts, meaning existing assets can’t be reused. While the open-source version is free, advanced features like hosted execution are only available in paid tiers.
Best for
Developer teams testing modern APIs and microservices that need scripting flexibility.
Pros
- Lightweight and easy to start with.
- YAML/JavaScript scripting for flexible scenarios.
- Supports GraphQL, gRPC, Kafka, and WebSockets.
- Playwright integration for browser-based tests.
- Scales with Pro and Cloud editions.
Cons
- Requires scripting skills; no no-code option.
- No JMeter or Gatling script compatibility.
- Limited reporting compared to enterprise tools.
- No built-in APM integrations.
Protocols supported
HTTP/HTTPS, REST, WebSocket, GraphQL, gRPC, Kafka.
7. Locust — Python-Based Load Testing with Flexible Scripting
Locust is an open-source load testing tool that uses Python code to define user behavior. Instead of configuring scenarios through a UI, testers write scripts that describe how virtual users interact with APIs. This makes Locust highly flexible and a good fit for teams that want to build complex or custom workflows.
For scalability, Locust supports distributed load generation, where multiple machines work together to simulate large numbers of requests. The commercial edition, Locust.cloud, simplifies this by offering hosted load generators, a web UI, and managed infrastructure.
The main drawback is its reliance on Python. Teams without programming expertise may struggle, and there is no built-in recorder for quick scenario creation. Reporting is functional but less advanced than enterprise-focused tools like PFLB or LoadRunner, and long-term storage of test results is limited in the cloud version.
Best for
Engineering teams with Python expertise that need a flexible, scriptable API load testing tool.
Pros
- Full control with Python scripting.
- Distributed testing for large-scale scenarios.
- Open-source and free to use.
- Locust.cloud adds hosted infrastructure and dashboards.
- Strong documentation with code examples.
Cons
- Requires Python knowledge; steep learning curve for non-developers.
- No built-in recorder or no-code builder.
- Limited reporting and analytics compared to enterprise platforms.
- Locust.cloud does not support private deployments.
Protocols supported
HTTP/HTTPS, REST, WebSocket, gRPC, Kafka.
8. Postman — Functional Testing with Basic Load Capabilities
Postman is best known as a functional API testing tool, but it also supports small-scale load testing through reusable collections. Its simple interface allows teams to define requests, organize them into collections, and run automated tests without writing code. For early development and QA, this makes Postman a convenient starting point.
While Postman can simulate concurrent API calls, it is not built for high-scale performance testing. The tool’s reporting and analytics are limited, and there is no distributed infrastructure to handle large traffic scenarios. Still, Postman is widely used as part of the development workflow and can serve as a lightweight option for teams who want to validate APIs before moving to heavier tools.
Best for
Small teams or developers already using Postman for functional testing who need limited load testing.
Pros
- Beginner-friendly, no coding required.
- Easy to organize and reuse API collections.
- Affordable pricing with a generous free tier.
- Popular tool with strong community adoption.
Cons
- Not designed for large-scale load testing
- Limited reporting and advanced analytics
Best For:
- Not designed for large-scale API load testing.
- Limited analytics and performance reporting.
- No distributed or cloud-based load generation.
Protocols supported
REST, SOAP, GraphQL (via API requests).
9. SoapUI — Functional API Testing with Limited Load Features
SoapUI is primarily known as a functional testing platform for APIs, especially SOAP and REST services. It includes basic load testing features that let teams run performance scenarios against APIs, making it a good option for QA teams that already rely on SoapUI for validation. Its user-friendly interface and strong documentation make it approachable even for beginners.
However, SoapUI is not optimized for large-scale load testing. Distributed execution requires significant setup, reporting is limited compared to dedicated performance tools, and it lacks support for modern protocols like gRPC or GraphQL. For many teams, SoapUI works best as a secondary tool for quick checks rather than as the main load testing solution.
Best for
QA teams focused on SOAP and REST functional testing with occasional light performance checks.
Pros
- Easy-to-use interface with strong documentation.
- Good for functional testing of SOAP and REST APIs.
- Free open-source edition available.
- Active community and tutorials.
Cons
- Limited scalability for true load testing.
- Outdated interface compared to modern platforms.
- No support for gRPC, GraphQL, or WebSockets.
- Reporting and analytics are very basic.
Protocols supported
SOAP, REST, HTTP/HTTPS.
10. Loader.io — Simple Cloud-Based Load Testing
Loader.io is a straightforward cloud-based load testing tool designed for small applications and quick performance checks. After verifying domain ownership, teams can run tests by sending thousands of concurrent requests to their API or web app. The setup is fast, and real-time reporting lets users watch how their system responds under traffic spikes.
The tool’s simplicity is both its strength and limitation. Loader.io is easy to start with and even offers a free plan, but it lacks advanced features like detailed analytics, scripting, or protocol diversity. It is best suited for lightweight validation rather than enterprise-scale testing.
Best for
Startups and small teams needing a quick, no-frills way to test API performance.
Pros
- Very simple setup with cloud-based execution.
- Free tier available for small projects.
- Real-time reporting during tests.
- No coding required.
Cons
- Limited scalability compared to enterprise tools.
- No advanced scripting or scenario customization.
- Lacks modern protocol support beyond HTTP/REST.
- Reporting is basic with minimal analytics.
Protocols supported
HTTP/HTTPS, REST.
Conclusion
The tools we reviewed each bring different strengths to the table: open-source options like JMeter, k6, and Locust give flexibility at low cost, while enterprise platforms such as PFLB and LoadRunner offer scalability, advanced analytics, and managed infrastructure.
In the end, the best API load testing tool depends on your needs. Consider your team’s skills, the protocols you must support, your budget, and how easily a tool fits into your CI/CD pipeline. Whenever possible, start with free tiers or trials, run pilot tests, and choose the platform that balances reliability, scalability, and usability for your specific goals.