In modern distributed systems, choosing the right communication protocol is crucial for scalability, performance, and flexibility. gRPC has become a popular choice thanks to its efficiency and language support, but it’s not always the best fit for every project. This guide explores the top gRPC alternatives, comparing their features, use cases, and best applications.
Whether you’re a developer, architect, or product manager, this article will help you evaluate gRPC competitors, understand their strengths, and select the right protocol for your project’s needs.
Key Takeaways
What Is gRPC?
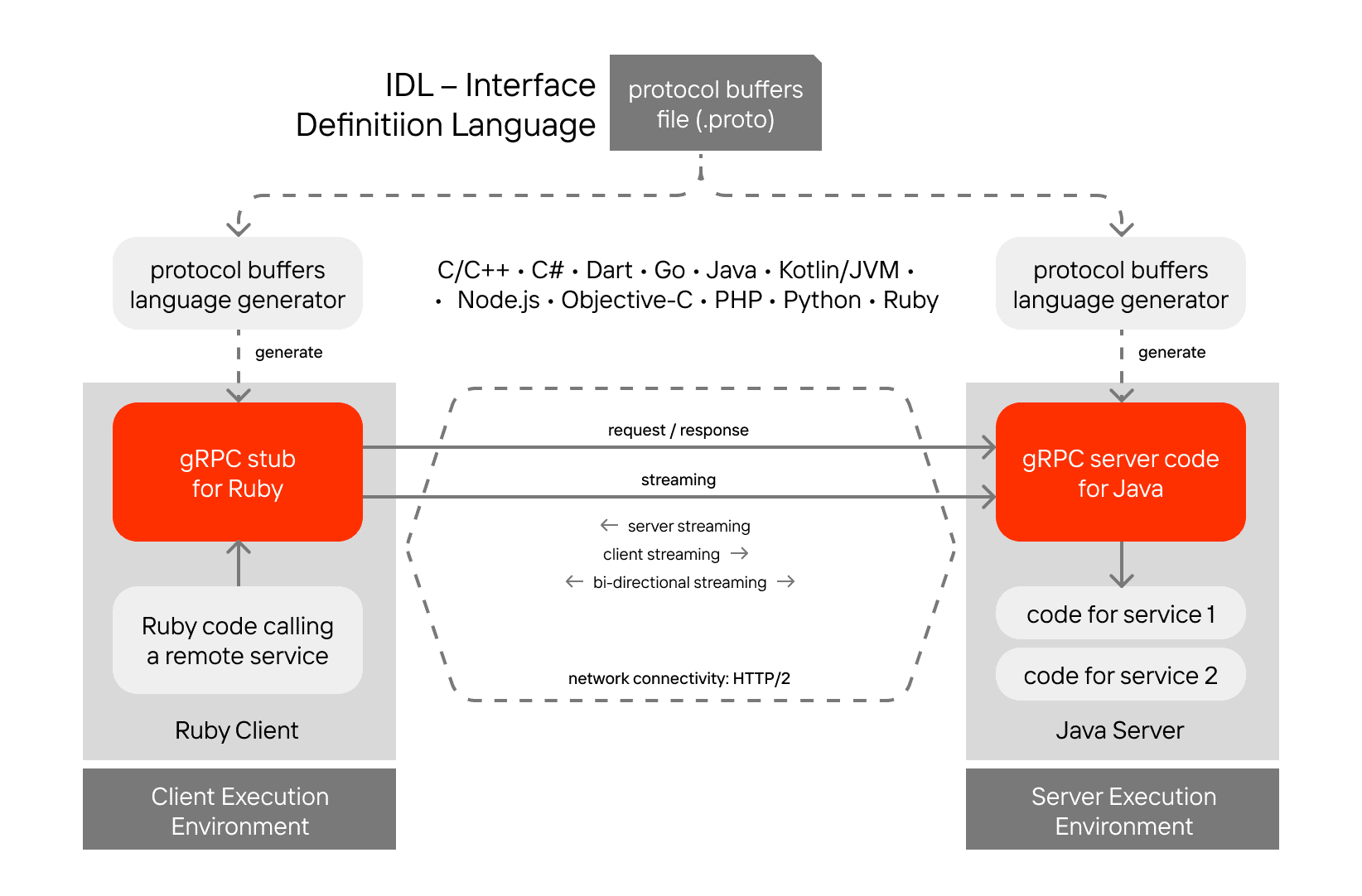
At its core, gRPC is a modern way for applications to talk to each other. Instead of sending clunky text-based messages back and forth, it lets one program call a function in another program, even if it’s running on a different machine, almost as if it were local.
Created by Google, gRPC is open source and built on top of HTTP/2, which means it benefits from faster connections, smaller messages, and even the ability to stream data in both directions. To keep things lightweight, it usually relies on Protocol Buffers (Protobuf), a compact format that’s quick to process and works across multiple languages.
This combination makes gRPC especially popular for microservices, real-time systems, and projects where speed and efficiency matter more than simplicity.
Best gRPC Alternatives You Should Know
While gRPC is fast, lightweight, and powerful, it’s not always the best fit. Different projects demand different approaches depending on performance needs, client support, or architectural complexity.
Below is a list of the most widely used alternatives to gRPC, each with its own strengths and use cases.
1. Apache Thrift

Description:
Apache Thrift started at Facebook and was later open-sourced through the Apache Software Foundation. It’s both an interface definition language (IDL) and a communication framework, designed to make it easier for applications written in different languages to work together. Like gRPC, it provides cross-language RPC, but unlike gRPC it gives developers more flexibility with serialization formats, not just Protocol Buffers.
Key features:
Best for:
Distributed systems where different services are written in different languages and need to communicate efficiently.
Why use it?
If your project requires speed but you don’t want to be locked into one serialization method, Thrift gives you options. It’s a strong choice when you need both performance and flexibility, especially in complex multi-language environments.
2. REST

Description:
The gRPC alternative called REST (Representational State Transfer) is the most widely used way of building APIs today. It relies on standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE, with data typically exchanged in JSON or XML. Because it’s simple, human-readable, and works directly over the web, REST quickly became the default choice for browser-based clients and public APIs.
Key features:
Best for:
Public APIs, web applications, and services that need to be easily consumed by browsers, mobile apps, or third-party developers.
Why use it?
REST is everywhere. If your priority is compatibility, simplicity, and quick adoption, REST is the safest bet. While it doesn’t offer the raw performance of gRPC, its universality and ease of use make it the go-to option for most web-facing projects.
3. GraphQL
Description:
GraphQL was developed by Facebook to solve a common problem with REST APIs: over-fetching and under-fetching data. Instead of receiving too much or too little information, clients can request exactly what they need in a single query. It acts more like a query language for APIs rather than a fixed set of endpoints.
Key features:
Best for:
Applications where the front end (mobile or web) needs flexibility and efficiency in how it requests data, especially when bandwidth or performance is limited.
Why use it?
GraphQL is ideal when different clients consume the same API in different ways. For example, a mobile app might request lightweight data, while a desktop client fetches more detailed information. With GraphQL, you only ask once and get exactly what you need.
4. JSON-RPC

Description:
JSON-RPC is a lightweight remote procedure call protocol that uses JSON for data encoding. Unlike gRPC or Thrift, it doesn’t require complex setup or an IDL, you just send a JSON object describing the method to call and the parameters. It’s simple, stateless, and can run over HTTP, WebSocket, or even raw TCP.
Key features:
Best for:
Small projects, quick prototypes, or internal tools where simplicity and speed of implementation matter more than performance.
Why use it?
If you want something that’s easy to set up and you’re already comfortable working with JSON, JSON-RPC is a great fit. It avoids the complexity of gRPC while still giving you a structured way to make remote calls.
5. Akka gRPC

Description:
Akka gRPC is part of the Akka ecosystem, designed for developers working with Scala or Java. It combines gRPC’s high-performance RPC capabilities with Akka Streams, giving teams a powerful tool for building reactive, message-driven systems. If you’re already in the Akka world, this integration makes it easy to adopt gRPC without leaving the reactive programming model.
Key features:
Best for:
Reactive systems, event-driven applications, and JVM-based projects that already use Akka for concurrency and messaging.
Why use it?
Akka gRPC is the natural choice if your team is invested in the Akka ecosystem. It blends the strengths of gRPC with Akka’s concurrency model, making it ideal for building highly scalable, resilient applications.
6. Socket.IO
Description:
Socket.IO is a JavaScript library that enables real-time, bidirectional communication between clients (usually browsers) and servers. Built on top of WebSockets, it also provides fallbacks to other transport methods when WebSockets aren’t available, ensuring stable connections across different environments.
Key features:
Best for:
Web and mobile apps that rely on live updates, such as chat applications, online games, or collaborative tools.
Why use it?
Socket.IO is a developer-friendly way to add instant, low-latency communication to your project. If you need real-time features without diving into the complexity of custom WebSocket handling, this library makes it quick and reliable.
7. Apache Avro
Description:
Apache Avro is a data serialization system that’s part of the Hadoop ecosystem. It’s designed for compact, fast, and schema-driven data exchange. Unlike gRPC or Thrift, Avro focuses on serialization rather than being a full RPC framework, making it especially popular in big data and streaming platforms like Apache Kafka.
Key features:
Best for:
Data pipelines, streaming platforms, and big data environments where efficient serialization and schema evolution are essential.
Why use it?
If your project involves handling large volumes of structured data, especially with Kafka or Hadoop, Avro is a natural fit. It ensures fast, compact serialization while allowing schemas to evolve without breaking existing data.
8. ZeroMQ

Description:
ZeroMQ (also known as ØMQ) is a high-performance asynchronous messaging library. Unlike gRPC or REST, it isn’t a full RPC framework but rather a flexible toolkit for building custom messaging patterns. Developers often describe it as “sockets on steroids” because it extends standard sockets with features like queuing, pub/sub, and request/reply messaging.
Key features:
Best for:
Custom distributed systems that need raw performance, flexible messaging patterns, and minimal latency.
Why use it?
ZeroMQ is ideal when you want maximum control over your communication layer. It doesn’t force you into a strict model like gRPC does, instead, it gives you the building blocks to design the messaging patterns that fit your architecture.
9. RSocket
Description:
RSocket is a binary communication protocol created by Netflix, designed around reactive streams principles. Unlike traditional request/response models, it supports multiple interaction patterns, including streaming and bidirectional communication, while handling backpressure natively. This makes it a strong fit for modern, reactive microservices.
Key features:
Best for:
Reactive microservices, streaming applications, and systems that need efficient handling of high-throughput communication.
Why use it?
RSocket is a great option when you need more than just request/response. Its support for streaming and backpressure makes it ideal for scalable, event-driven architectures where data flows continuously.
10. Solace PubSub+

Description:
Solace PubSub+ is an advanced event-broker platform designed for enterprise-scale messaging. It supports multiple communication styles, from publish/subscribe to request/reply, and works seamlessly across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments. Unlike lighter frameworks like gRPC, it’s built with enterprise reliability and large-scale event distribution in mind.
Key features:
Best for:
Large organizations that need reliable, high-performance event streaming across complex, hybrid infrastructures.
Why use it?
If your project demands enterprise-grade reliability and the ability to integrate multiple messaging protocols, Solace PubSub+ is one of the strongest alternatives besides gRPC. It’s particularly suited for industries like finance, telecom, and transportation where data flow must be fast and uninterrupted.
11. WebSockets

Description:
WebSockets is a communication protocol that provides full-duplex, persistent connections between a client (often a browser) and a server. Unlike HTTP, which closes after each request, a WebSocket connection stays open, allowing both sides to send data whenever needed. This makes it a go-to choice for real-time, interactive applications.
Key features:
Best for:
Real-time applications like chat systems, online gaming, collaborative tools, stock tickers, and live dashboards.
Why use it?
If you need instant, two-way communication between a browser and server, WebSockets is the simplest and most widely supported choice. It’s easy to adopt and forms the backbone of many real-time web experiences.
gRPC Alternatives Comparison Table
Choosing between gRPC and its competitors isn’t always easy, each option comes with its own strengths and trade-offs. Some shine when simplicity and browser support matter, while others are built for high-throughput messaging or reactive systems.
To help you quickly compare, here’s a side-by-side look at the most popular alternatives, their communication style, data formats, and where they’re best used.
Consider PFLB’s gRPC Load Testing Tool
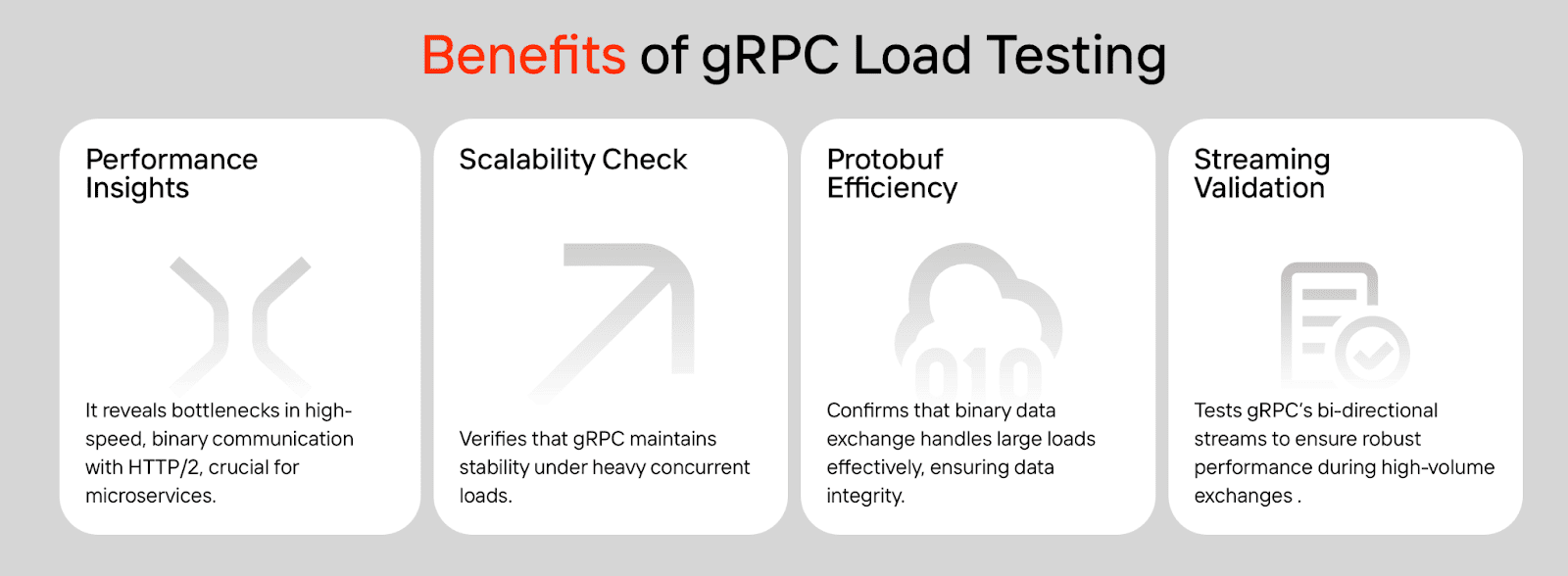
When evaluating gRPC and its alternatives, one key factor often gets overlooked: performance under real-world load. Even the most efficient protocol can fail to deliver if it isn’t tested against the scale and complexity of your production environment.
Learn more about how to test performance of gRPC or explore how PFLB helps enterprises validate their systems under real-world load.
PFLB is a performance testing company with 15+ years of experience helping enterprises validate the scalability and reliability of their systems. From banking platforms handling millions of transactions to telecom networks serving millions of subscribers, we’ve ensured mission-critical systems perform under pressure.
Our Expertise in gRPC Testing
Why Choose PFLB?
Our gRPC load testing tool is built to handle the complexity of modern protocols, giving your team:
Whether you’re just adopting gRPC or evaluating other communication protocols, PFLB’s expertise ensures your system not only works but performs at scale.
Conclusion
Picking the right communication protocol can make or break a project. While gRPC is powerful, the alternatives we’ve covered, from REST and GraphQL to ZeroMQ and WebSockets, each bring unique strengths to the table. The best choice depends on your system’s goals, whether that’s flexibility, simplicity, enterprise reliability, or raw speed.
And once you’ve chosen, don’t forget the final step: testing performance at scale. With PFLB’s expertise and dedicated gRPC load testing tool, you can be sure your system isn’t just functional, but ready to handle real-world demand.