When it comes to performance testing, not all user interactions are created equal. The difference between concurrent and simultaneous user testing may sound subtle, but it has a big impact on how well your system handles real-world scenarios. If you’re preparing your platform for anything from daily traffic to high-stakes launches, understanding these terms can help you choose the right testing strategy and avoid performance pitfalls.
This article will break down the differences between concurrent and simultaneous user testing, explore practical examples, and guide you on when and how to apply each method effectively.
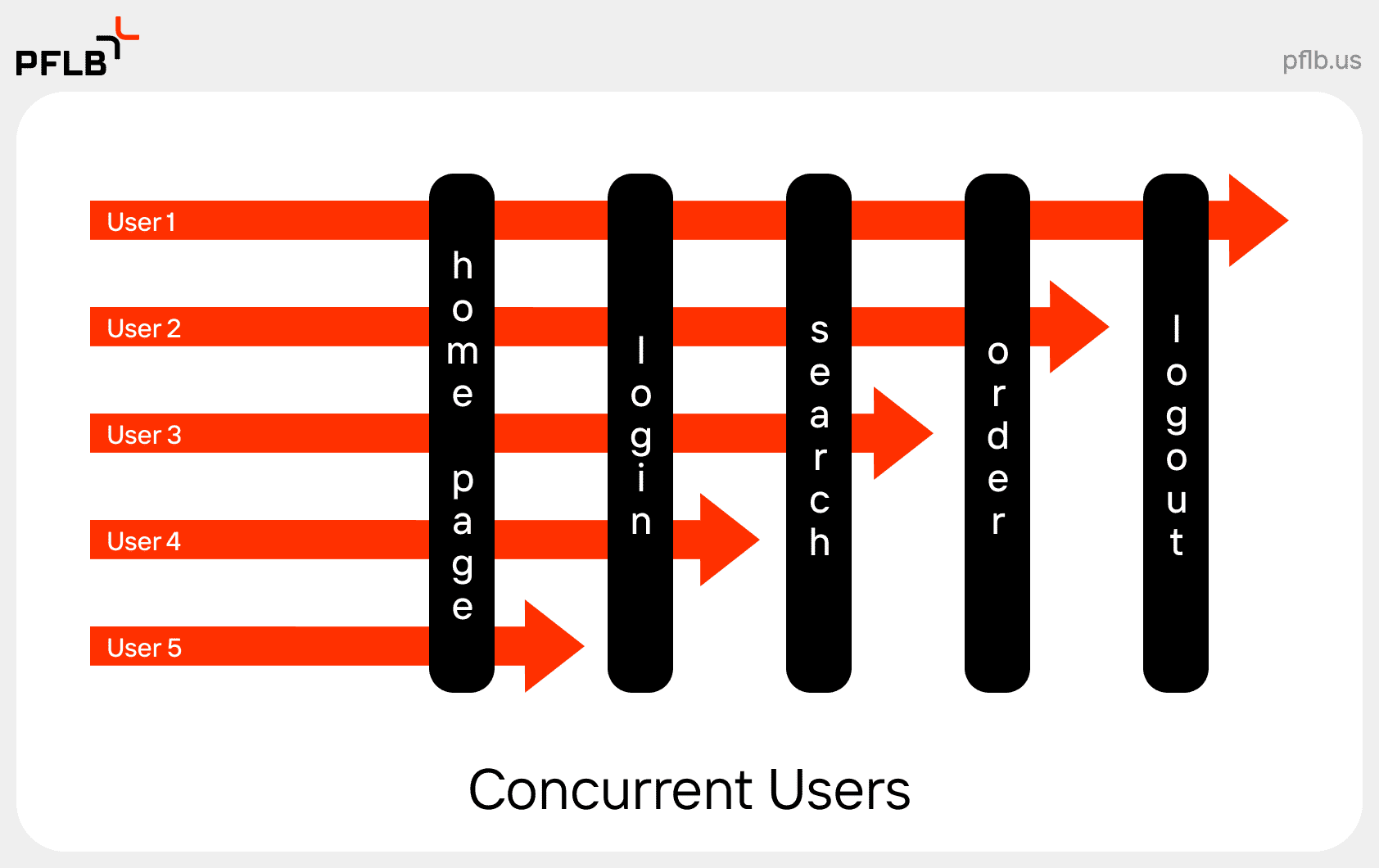
What Are Concurrent Users?
Concurrent users are individuals who interact with a system or application within the same time frame, though they may not be performing the same actions simultaneously. In performance testing, this term refers to scenarios where multiple users are active on a platform, engaging with different features or completing varied tasks. These tasks could include browsing a website, filling out a form, downloading files, or navigating through different pages—each action occurring independently yet within a shared timeframe.
For example, imagine an e-commerce website during a sale. One user might be adding items to their cart, another could be processing a payment, while others are simply browsing through products. All of these users are considered concurrent users because their sessions overlap, even if their actions differ.
Testing for concurrent users is essential to evaluate how a system manages resource allocation, server load, and responsiveness under real-world usage patterns. It helps identify potential bottlenecks and ensures that the platform remains stable and efficient even during periods of high traffic.
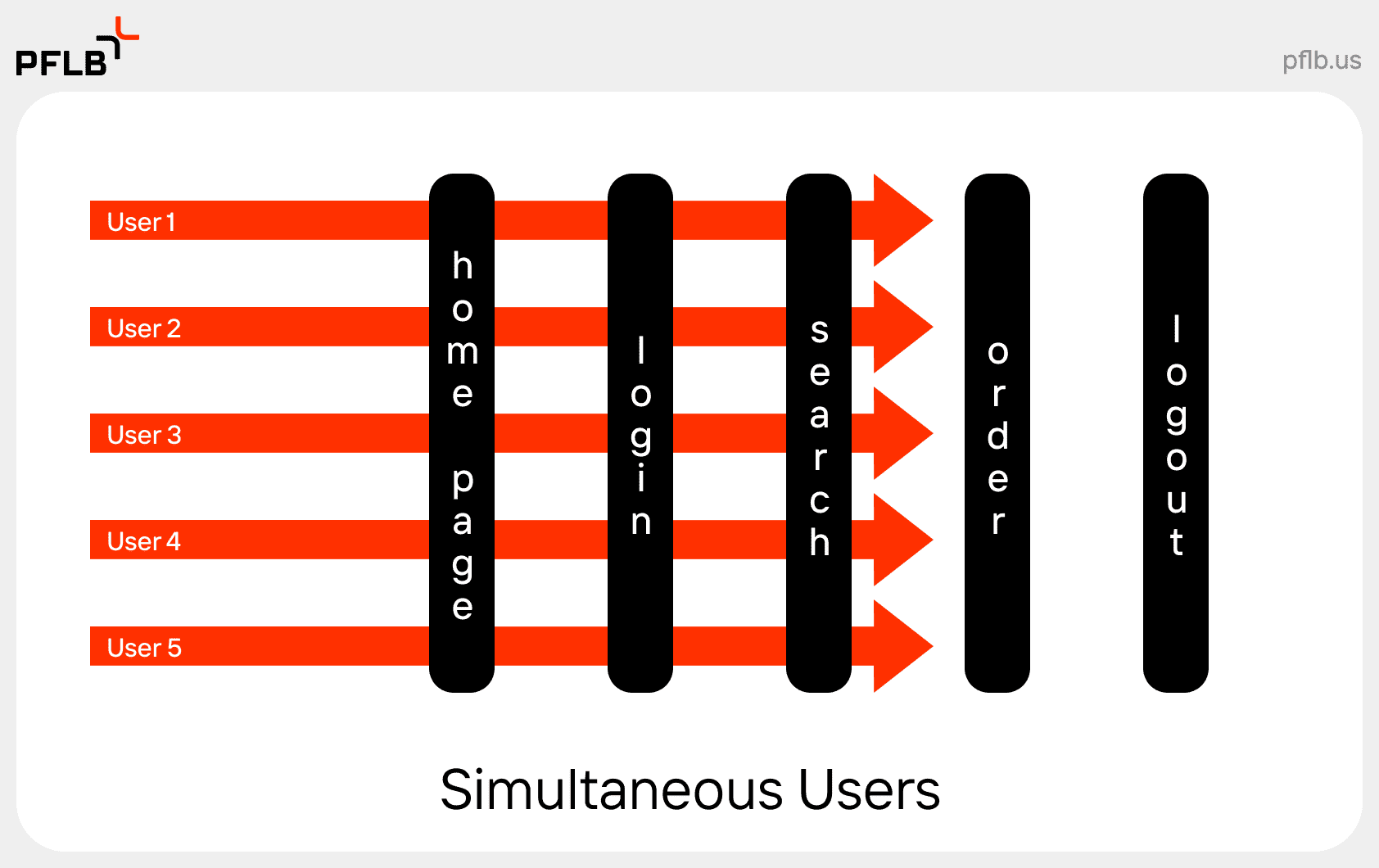
What Are Simultaneous Users?
Simultaneous users are those who perform the same action at precisely the same moment within a system or application. Unlike concurrent users, who may be active on a platform simultaneously but not necessarily executing the same tasks, simultaneous users initiate identical actions at exactly the same time. This distinction is crucial in concurrent vs. simultaneous user testing, as each method evaluates different performance aspects of a system.
A classic example of simultaneous users is during a flash sale on an e-commerce site, where hundreds of users click the “Purchase” button at the same second. This scenario tests the system’s ability to handle peak loads without crashing or experiencing performance lags. By simulating simultaneous vs concurrent users, testers can identify potential weaknesses in how the system manages identical, high-volume requests.
Testing with simultaneous users is particularly valuable in scenarios where split-second actions matter, such as online bidding platforms or live event registrations. It ensures that the system maintains performance and stability even under extreme pressure.
Concurrent Users Testing
When conducting concurrent users in performance testing, it is essential to replicate real-world scenarios where multiple users interact with a system simultaneously, but not necessarily performing the same actions. This type of testing helps evaluate how well a platform manages varying loads and maintains performance under typical and peak conditions.
When setting up concurrent user testing, consider the following critical factors:
Testing with concurrent users provides insights into the system’s ability to handle diverse user actions within the same timeframe. It is an effective strategy for identifying bottlenecks and ensuring consistent performance under realistic conditions. Learn more about what is concurrency testing.
Simultaneous User Testing
Simultaneous user testing involves evaluating how a system performs when multiple users execute the same action at exactly the same time. Unlike concurrent users vs simultaneous users testing, where different actions may occur within the same time frame, simultaneous testing focuses on synchronized actions to simulate peak load scenarios.
When setting up tests for simultaneous users, consider the following critical aspects:
Simulating simultaneous vs concurrent scenarios can help identify performance bottlenecks and ensure the system remains reliable during high-demand events, such as flash sales or live streaming sessions. In more complex environments, techniques like chaos engineering are also used to introduce controlled failures, helping teams evaluate how systems behave under unpredictable conditions.
Concurrent & Simultaneous User Load Testing with PFLB
When it comes to handling both concurrent and simultaneous user testing, PFLB offers more than just a standard solution. The website load testing tool is designed to replicate diverse real-world scenarios, from the everyday hustle of varied user interactions to the intense, synchronized pressure of peak events. Meanwhile, the API load testing tool dives deep into backend performance, ensuring your system remains resilient and responsive no matter how demanding the situation.
Conclusion: Testing for Real-World Scenarios
Real-world traffic isn’t predictable; sometimes, it’s a steady stream of varied user actions, while at other times, it’s a sudden rush of synchronized clicks. Effective performance testing anticipates both scenarios, offering insights that go beyond basic metrics to address real usability and stability challenges.
The goal is not merely to test limits but to create a robust system that adapts dynamically to changing demands. By implementing continuous performance testing and focusing on realistic scenarios, you can transform testing into a proactive measure that keeps your platform not only functional but also consistently efficient and user-friendly, even during peak demands. When selecting your performance testing toolkit, you’ll need to evaluate which solutions best fit your specific requirements.
Read next: Which load testing tool is better: K6 or JMeter to understand the strengths and differences between these popular options.