Software interfaces were invented to integrate applications. They work as a kind of port through which you can connect to third-party software and interact with it, for example, send a request to a database and get a response. To make the interface usable for other software, there have to be some rules—what requests can be sent to the application and what the responses will be.
Several standard platforms and protocols are used to create software interfaces. One of the most well-known systems is REST API, based on a popular Internet protocol HTTP. However, there are other ways to organize communication between applications, and one of them is the gRPC framework.
Key Takeaways:
What Is gRPC
gRPC is a platform that helps create software interfaces based on Remote Procedure Call (RPC) (learn more about what is gRPC). gRPC was originally developed by Google but was later converted to open-source software. Unlike REST API, the system allows third-party subprograms to run as if they were run locally, although in fact they may be running on a different computer. This approach is faster and simpler than traditional HTTP requests.
The API created with gRPC consists of a server and a client. The client generates procedure calls, and the server processes them. There may be a variety of such interactions, as gRPC initially supports different programming languages and lets clients of different applications communicate with the server. Architectural differences provide a framework with a speed higher than in REST API. The thing is, the messages exchanged by applications under gRPC are smaller. In addition, HTTP/2 allows a full-fledged, bidirectional flow of data exchange, instead of acting in the “request-response” paradigm, as in HTTP 1.1.
Testing gRPC’s performance requires tailored approaches to capture its unique strengths and potential limitations.
You can also read our detailed comparison of gRPC vs REST, , and if you’re weighing broader options beyond these two, browse gRPC alternatives for side‑by‑side use cases and trade‑offs.
Core Objectives of gRPC Performance Testing
The goal of gRPC load testing is to ensure the API can handle real-world scenarios efficiently while maintaining stability under varying loads. Here are some key objectives:
How to Test gRPC Performance
No matter how fast and progressive gRPC is, do not forget to check its speed. If the API is not working well, you may lose some requests, along with some users of your application. Therefore, it is important to regularly check performance by defining API benchmarks, which include:
The main difference between gRPC performance testing tool and that of other parts of an application or site is the necessity to check the complete two-way data exchange. Its analysis requires special methods and tools, because the testing involves two parties. It is important not only to check the ability of the server to handle many requests from the client, but also the client’s ability to “digest” the data stream from the server. We have selected the best gRPC testing tools for you.
Methods and Strategies for gRPC Performance Testing
Simulate Real-World Workloads
Begin by recreating realistic client-server interactions. This involves testing various types of gRPC calls:
By simulating these scenarios, you can evaluate how the system behaves under typical workloads.
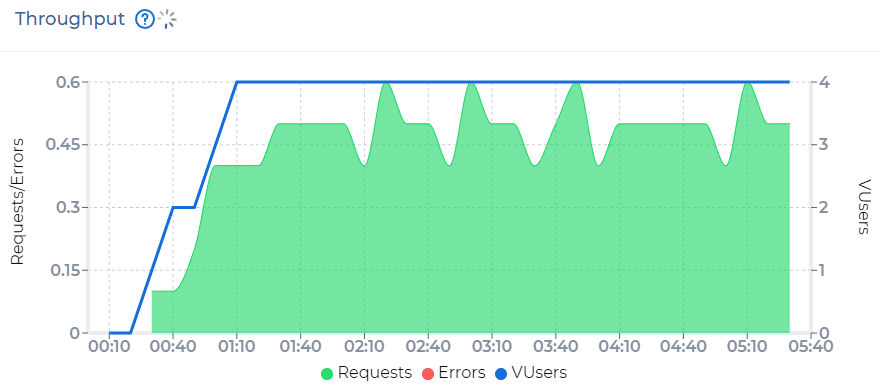
Load Testing for Throughput and Latency
Measure how many queries per second (QPS) the system can handle while maintaining acceptable latency. gRPC load testing tools like PFLB allow you to define test parameters such as the number of concurrent clients, message sizes, and call types to understand the system’s performance envelope.
Stress Testing to Identify Limits
Push the system to its breaking point by increasing the number of concurrent streams or data flows. Focus on:
Test Protocol Buffers Serialization
Since gRPC uses Protocol Buffers for serialization and deserialization, it’s crucial to test how efficiently your Protobuf schemas handle large or complex data. Inefficient schemas can introduce delays and resource bottlenecks.
HTTP/2-Specific Testing
Test the impact of HTTP/2’s multiplexing and header compression on gRPC performance. Verify that connections are reused efficiently and that the server can handle multiple streams over the same connection.
Monitor Resource Utilization
Monitor CPU time, memory, and network bandwidth during tests to ensure that your gRPC implementation scales efficiently without overloading resources.
Performance Profiling with Observability Tools
Use observability tools like Grafana to gather real-time insights into latency, QPS, and resource utilization. Profiling data helps pinpoint bottlenecks and areas for optimization.
Automate Testing for Consistency
Automate gRPC performance tests using continuous integration tools. Regular testing ensures that updates or changes to your API don’t inadvertently degrade performance.
Tools like PFLB support automated testing pipelines, ensuring consistency in performance tests as your system evolves.
How to Set Up gRPC service for performance testing
Before diving into load testing gRPC processes, you need to set up a functioning gRPC server and client. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process using Python, from installing the required tools to creating a simple gRPC testing client and server.
Step 1: Install gRPC for Python
To begin, install the necessary Python packages for gRPC using pip:
pip install grpcio grpcio-tools
The grpcio package provides the core gRPC library, while grpcio-tools helps compile Protocol Buffers (Protobuf) files into Python code.
Step 2: Define the Service Interface in a Protocol Buffers File
Create a .proto file to define your gRPC service. For example, let’s create a service called TestService with a method GetMessage that takes a Request message and returns a Response message.
syntax = "proto3";
service TestService {
rpc GetMessage(Request) returns (Response);
}
message Request {
string name = 1;
}
message Response {
string message = 1;
}
Save this file as test_service.proto.
Step 3: Generate Python Code from the .proto File
Use grpcio-tools to compile the .proto file into Python code:
python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I. --python_out=. --grpc_python_out=. test_service.proto
This command generates two files:
Step 4: Implement the gRPC Server
Create a Python script (server.py) to implement and run the gRPC server:
import grpc
from concurrent import futures
import test_service_pb2
import test_service_pb2_grpc
# Implement the service
class TestServiceServicer(test_service_pb2_grpc.TestServiceServicer):
def GetMessage(self, request, context):
return test_service_pb2.Response(message=f"Hello, {request.name}!")
def serve():
server = grpc.server(futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10))
test_service_pb2_grpc.add_TestServiceServicer_to_server(TestServiceServicer(), server)
server.add_insecure_port("[::]:50051")
print("Server is running on port 50051...")
server.start()
server.wait_for_termination()
if __name__ == "__main__":
serve()
This script:
Step 5: Create a gRPC Client
Write a Python script (client.py) to interact with the gRPC server:
import grpc
import test_service_pb2
import test_service_pb2_grpc
def run():
with grpc.insecure_channel("localhost:50051") as channel:
stub = test_service_pb2_grpc.TestServiceStub(channel)
response = stub.GetMessage(test_service_pb2.Request(name="gRPC Tester"))
print(f"Server response: {response.message}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
run()
This script:
Step 6: Test Your Setup
python server.py
python client.py
You should see the server respond with Hello, gRPC Tester!.
This setup forms the foundation for performance testing. Once your gRPC service and client are running, you can integrate performance testing tools like PFLB, ghz, or Fortio to evaluate your API’s throughput, latency, and scalability.
gRPC Performance Testing with PFLB
PFLB provides powerful tools for performance testing gRPC services, helping you measure throughput, latency, and scalability. Here’s a step-by-step guide to using PFLB for gRPC performance testing:
Step 1: Set up PFLB
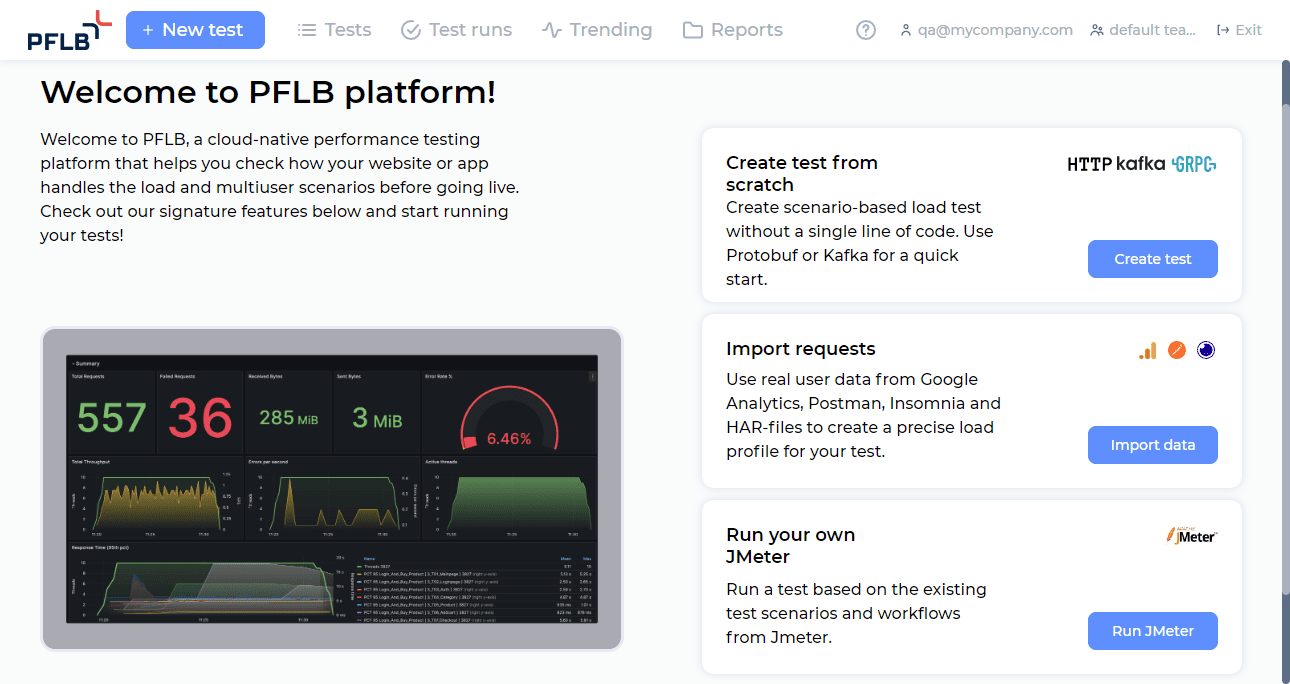
Simply visit the PFLB Platform login page, click Sign up, and fill in your email and password. Once you’ve created your account, the platform’s start screen will open, and you’ll automatically be added to the default team, ready to start testing.
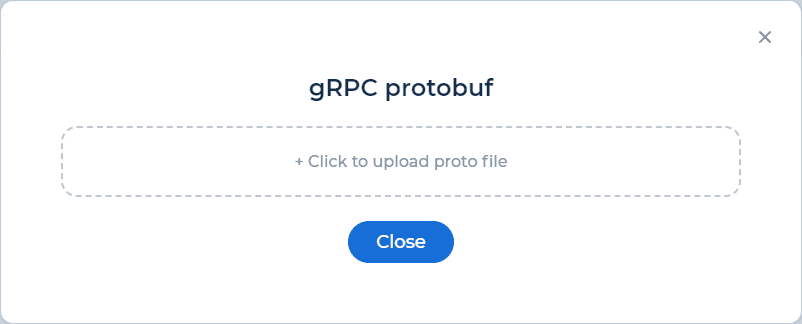
Step 2: Import Your .proto File
To begin testing your gRPC service, you’ll need to import the Protocol Buffers (Protobuf) file that defines the service’s methods and messages. The .proto file acts as a blueprint for the platform to understand your gRPC API.
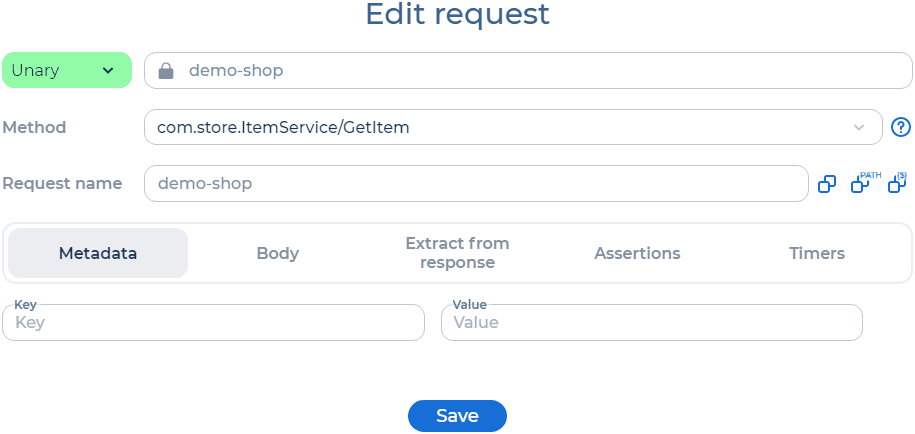
Step 3: Configure gRPC Requests for Testing
After importing the .proto file, configure the gRPC requests that will be used in your performance test:
Step 4: Design the Performance Test Scenario
Performance testing focuses on evaluating how your gRPC service handles different loads and conditions. Using the PFLB platform, you can configure scenarios to test:
Example configuration in PFLB:
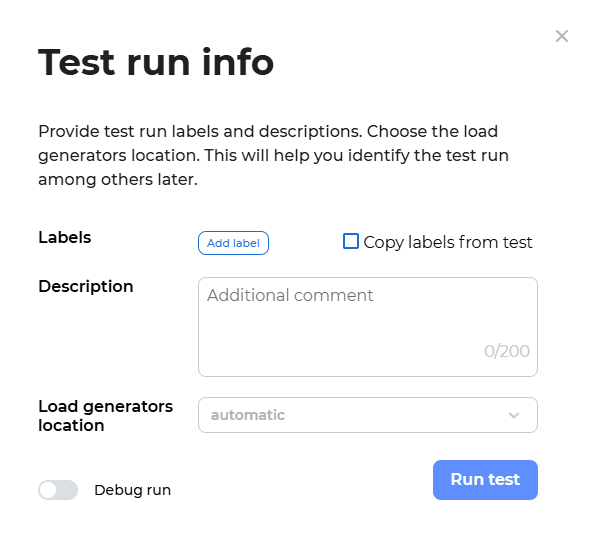
Step 5: Run the Performance Test
Once the test scenario is configured, execute the test:
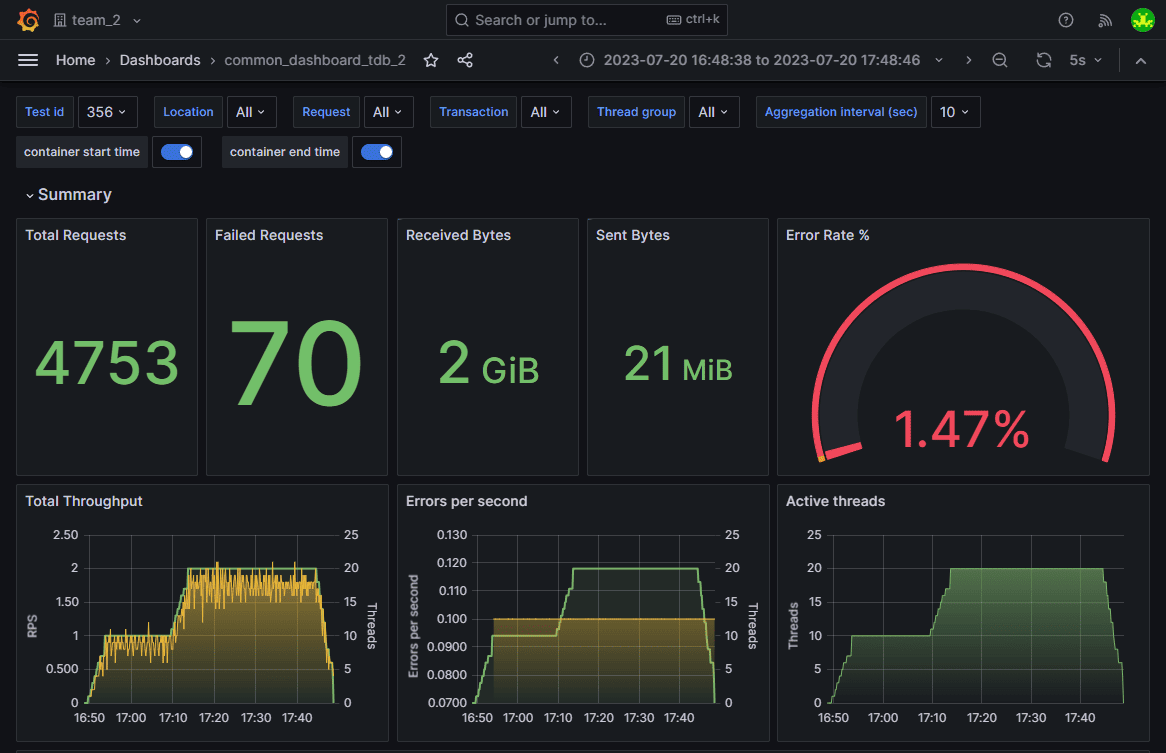
Step 6: Analyze and Optimize
After the test completes, review the detailed reports generated by PFLB. Focus on metrics such as:
Use these insights to optimize your gRPC service, such as:
Consider PFLB Your Best gRPC Performance Testing Provider
When it comes to ensuring your gRPC services perform at their peak, PFLB stands out as a trusted leader in performance testing. With years of expertise in delivering top-tier load testing solutions, PFLB has helped businesses optimize their APIs, streamline data exchange, and ensure reliability under heavy loads.
Why Businesses Trust PFLB
Ready to Experience the PFLB Advantage?
Join the businesses that trust PFLB for their gRPC performance testing needs. With a robust platform, expert solutions, and tools designed for real business benefits, PFLB helps you optimize your APIs for reliability, scalability, and user satisfaction.
Start your free trial today and take your gRPC performance to the next level.

 button to upload your
button to upload your