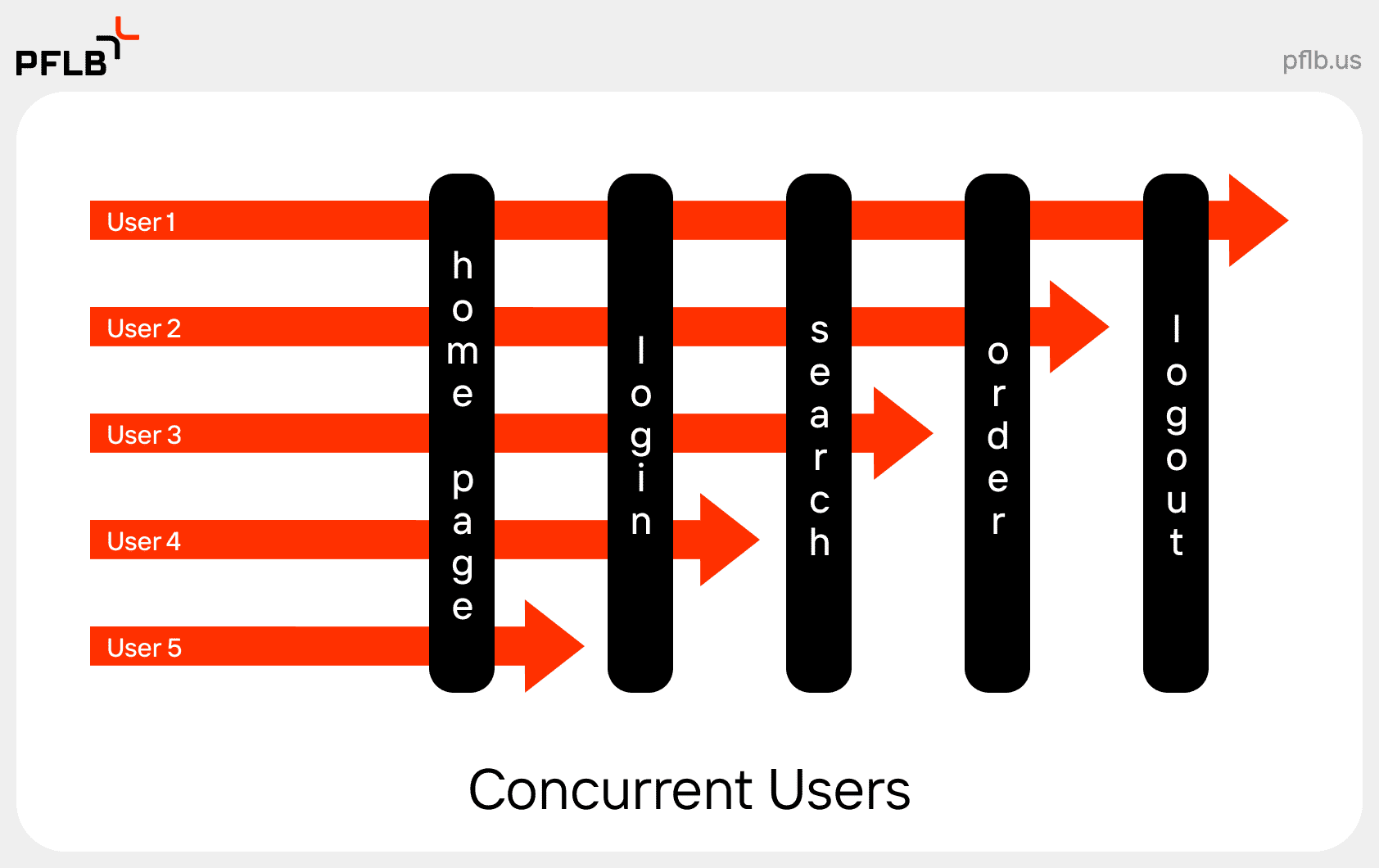
When multiple users interact with your application at the same time, will it still perform smoothly — or start to break down under pressure? That’s the kind of question concurrency testing is built to answer. By simulating simultaneous actions within your system, this method helps teams uncover bugs and bottlenecks that only show up under load.
In this article, we’ll explain what concurrency testing is, why it matters for software quality, and how it differs from other types of testing. You’ll also learn when and how to use it, explore real-world examples, and get a look at the most effective concurrency testing tools on the market today.
What is Concurrency Testing?
Concurrency testing is a type of performance test that evaluates how an application behaves when multiple operations or transactions occur at the same time. The goal is to identify issues like race conditions, deadlocks, or data corruption — problems that usually don’t surface during functional testing.
Here’s a concurrency testing example: Imagine an airline booking system where hundreds of users are trying to reserve the last few available seats on a flight. Without proper testing concurrency, the system might oversell those seats or crash entirely. That’s why integrating this testing early is essential for building stable and scalable applications.
For instance, in an online banking app, one user might transfer funds while another checks their balance — both actions rely on the same backend systems. If something goes wrong, it could lead to duplicate transactions, incorrect data, or worse.
A key distinction to understand is the difference between concurrency and parallelism. While both involve multitasking, concurrency is about managing multiple tasks at once (which may not run simultaneously), whereas parallelism means executing tasks at the exact same time — usually on multiple processors. Concurrency is more about structure; parallelism is about execution.
Understanding concurrency testing in software testing is critical for applications with high interaction rates, shared resources, or frequent database operations. It helps teams proactively catch subtle issues that often appear only under simultaneous load.
Want to learn more about performance testing? Learn what spike testing is and how it fits into the bigger picture.
Key Benefits of Concurrency Testing
When testing concurrency you ensure that your system can function reliably in real-world conditions. Below are the main benefits of concurrency testing and why it should be part of any serious QA or performance testing strategy.
Disadvantages of Concurrency Testing
While concurrency testing is powerful, it’s not without its challenges. Implementing it effectively requires expertise and infrastructure. Below are some common drawbacks teams encounter when incorporating concurrency tests into their workflows.
Increased Complexity
Designing and executing concurrent test cases is more complex than traditional testing. QA teams need to consider synchronization, timing, shared state management, and how multiple threads or processes interact. Even small misconfigurations can lead to misleading results.
Resource Limitations
Running meaningful concurrency tests often requires significant hardware or virtual infrastructure — especially when simulating thousands of concurrent users. Without proper planning, this can lead to skewed test outcomes or unintentional bottlenecks unrelated to the software itself.
Limited Test Coverage
Concurrency testing is great for exposing certain types of bugs, but it doesn’t cover every use case. Logical bugs, UI defects, or edge-case conditions unrelated to simultaneous use can go undetected, meaning teams must use it alongside other testing types like functional or load testing.
Increased Risk of Interference
When multiple processes or users run tests at the same time, they can unintentionally interfere with each other. For instance, shared test data can get overwritten or corrupted, leading to flaky results. It takes strong environment isolation and scripting discipline to avoid these pitfalls.
Concurrent Testing Methods
There are several methods used when testing for concurrency, each offering different levels of control and insight. The choice depends on your goals, infrastructure, and how early in the development cycle you want to catch concurrency issues.
How To Conduct Concurrency Testing
Setting up concurrency tests can feel overwhelming, but a structured approach helps ensure you get reliable, actionable results. Here’s a step-by-step process for testing concurrency effectively.
Best Concurrency Testing Tools
Choosing the right tool for testing concurrency depends on your application type, team expertise, and how deeply you need to simulate real-world load. Below are some of the most widely used tools for concurrency testing in software testing, including our in-house solution.
PFLB
PFLB offers an advanced performance testing platform built specifically for high-load and concurrent environments. Our proprietary engine is designed to simulate real user behavior at scale, with granular control over test parameters and precise reporting. Whether you’re stress testing banking apps or complex enterprise software, PFLB’s platform supports deep diagnostics and end-to-end visibility.
Use it as part of our complete performance testing services, or integrate it with your CI/CD pipeline to automate concurrency testing at every release stage.
Apache JMeter
JMeter is a popular open-source tool for load and concurrent testing. It supports multiple protocols (HTTP, FTP, JDBC, etc.) and allows you to simulate heavy loads on web applications, databases, and more. Its plugin ecosystem and scripting flexibility make it a go-to for many QA teams — especially for testing concurrent access to shared resources.
Gatling
Gatling is built in Scala and designed for high-performance load testing. Its DSL-style scripting makes it easy to model user behavior, and its real-time reports help teams quickly identify performance bottlenecks. Gatling is particularly strong at testing concurrency in APIs and web applications.
Locust
Locust is a Python-based tool that excels in writing user scenarios as code. It’s ideal for QA engineers who want customizable and readable test logic. Locust supports distributed testing and works well for simulating thousands of users making concurrent requests — perfect for services where user traffic is unpredictable or spiky.
BlazeMeter
BlazeMeter builds on JMeter and adds a polished UI, cloud execution, CI/CD integration, and enhanced analytics. It allows you to run massive concurrency tests without managing infrastructure. It’s a great option for teams that want the power of JMeter with enterprise-level scalability and support.
Final Thought
Concurrency issues aren’t rare. They’re just hard to spot until they cause real damage — corrupted data, locked resources, inexplicable behavior under load. By then, you’re not debugging. You’re firefighting.
At PFLB, we design concurrency tests for systems that can’t afford to be unpredictable — banking platforms, enterprise software, logistics tools. If you’re building in that territory, we’ll help you test like it.