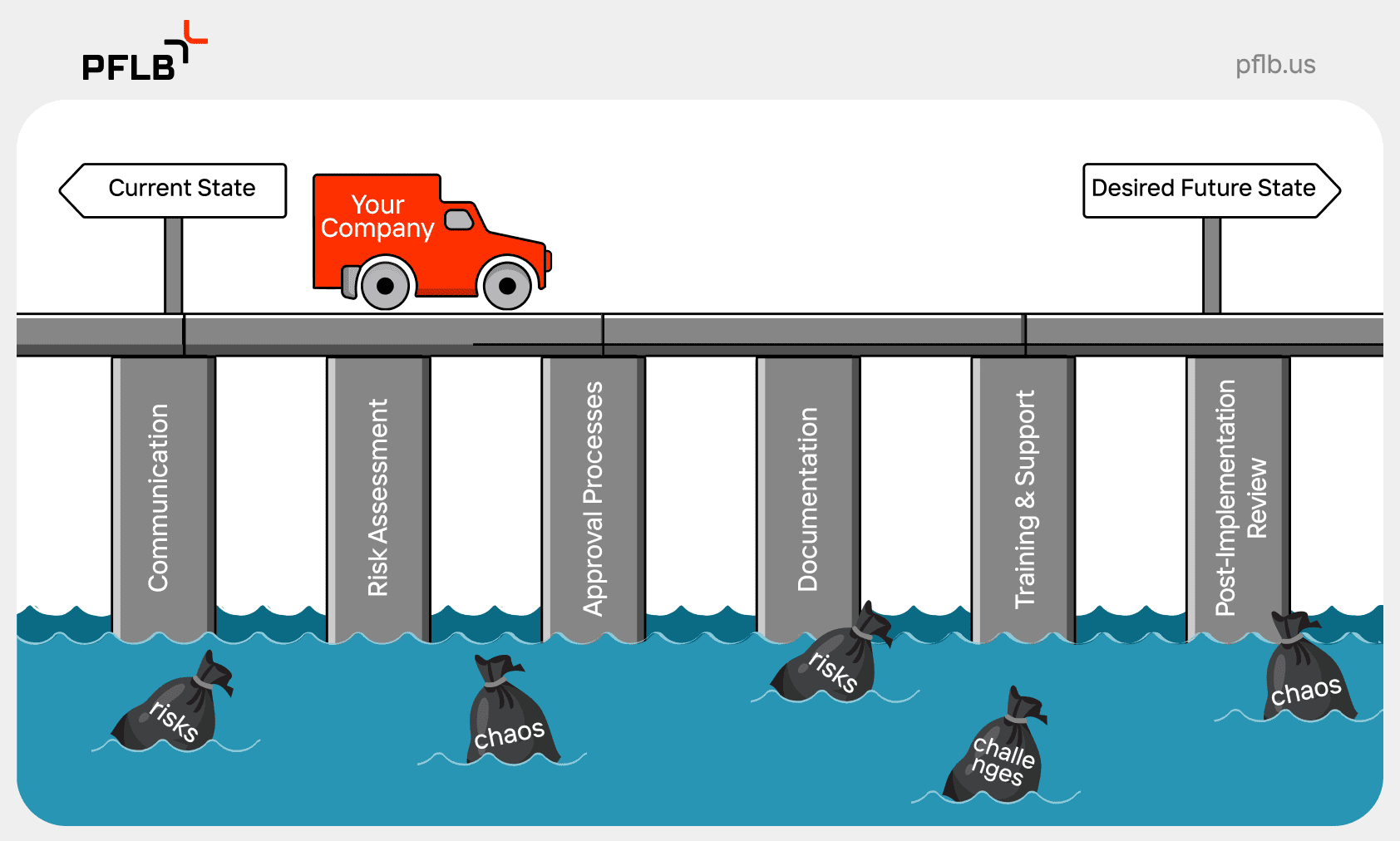
ITSM change management is essential for managing and implementing IT changes smoothly. It focuses on minimizing risks and aligning changes with business goals. In this guide, we’ll explore what ITSM change management entails, discuss its benefits, and provide practical tips for implementation.
Key Takeaways
What is ITSM Change Management?
ITSM change management is a key part of IT service management, concentrating on minimizing risks and ensuring successful implementation of changes. The primary objective of IT change management is to lower incidents and disruptions while enhancing the quality and reliability of IT services.
This entire change management process encompasses every aspect of change, including technology, people, and processes. It provides a structured framework that helps organizations handle changes systematically, ensuring smoother transitions and better alignment with business goals. Tracking changes and maintaining an auditable record enhances accountability and transparency within the organization, which is essential for effective organizational change management.
Effective change management is not just about controlling changes; it’s about enabling them in a way that supports business continuity and compliance with regulations. These practices can reduce service disruptions and improve overall service quality, making them vital to a comprehensive ITSM strategy.
Importance of ITSM Change Management
A robust change management process maintains a stable IT environment, crucial for delivering consistent and reliable services to users. Reducing the risks associated with IT changes ensures system stability and minimizes disruptions.
Effective change management aligns IT changes with business objectives. This alignment ensures that the changes support and enhance organizational growth, making it easier for the organization to respond to market demands and changes. Properly managed changes lead to enhancements in service quality and operational performance, contributing to overall business success.
Structured change management ensures planned and systematic executions, avoiding haphazard implementations that can disrupt services. A well-developed communication plan keeps all stakeholders informed, fostering trust and ensuring smoother transitions.
A solid change management process ultimately increases an organization’s agility and adaptability to new challenges through effective change management processes.
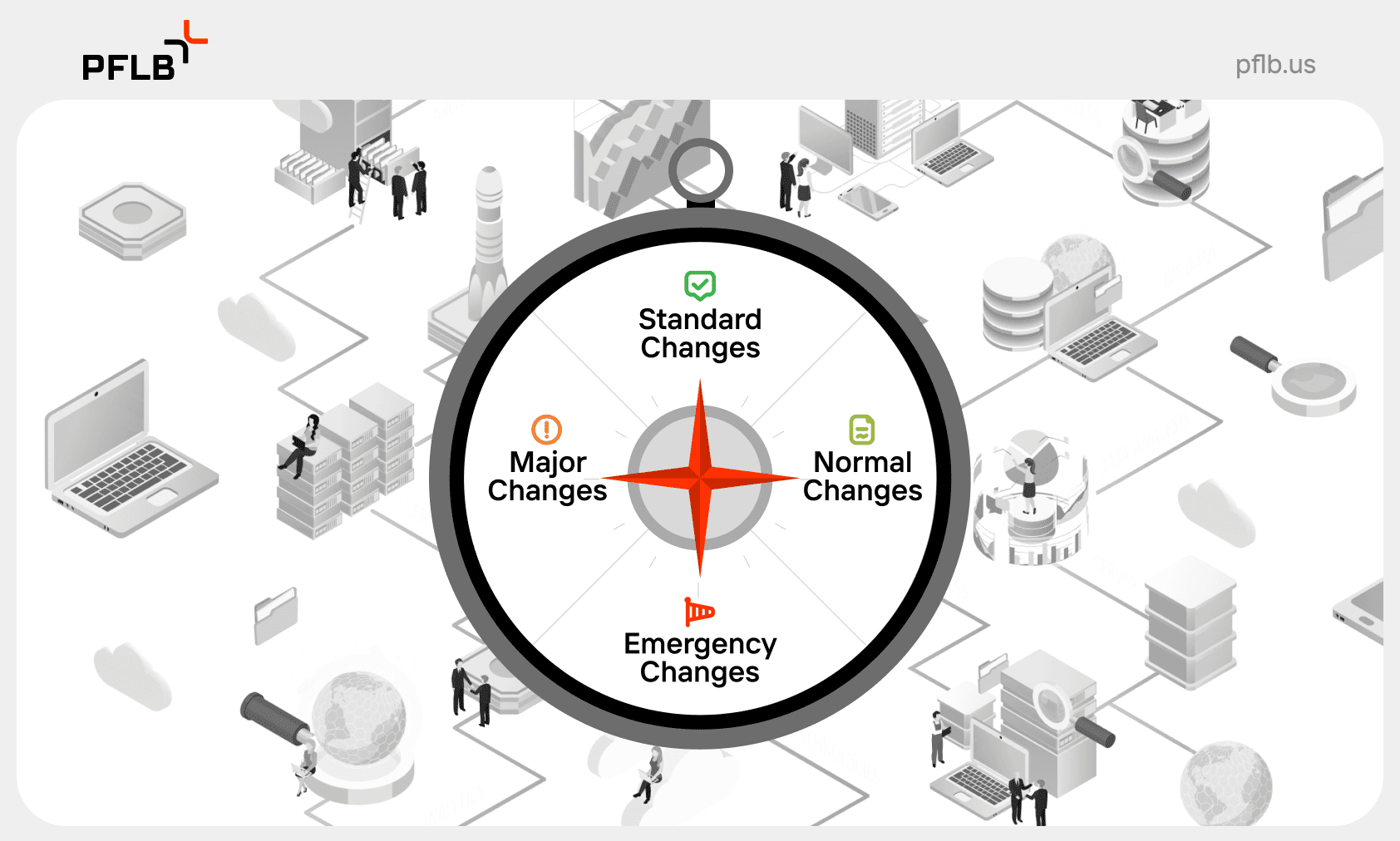
Types of Changes in ITSM
In ITSM, changes are categorized into three main types: standard, normal, and emergency. Each type requires a different approach, tailoring the change management process to specific needs and risks.
Standard Changes
Standard changes are routine, low-risk changes that can be implemented without extensive planning. These changes often follow pre-approved procedures and are frequently automated for efficiency.
Examples of standard changes include adding memory to a server, replacing a failing router, or installing new software on laptops.
Normal Changes
Normal changes are classified as non-emergency changes. They do not follow a pre-approved process. These changes require a thorough risk assessment and an approval process before implementation.
Examples include upgrading to a new content management system, performing hardware upgrades, migrating software, and making network configuration changes.
Emergency Changes
Emergency changes are urgent changes needed to address critical issues such as security breaches or system outages. These changes are typically implemented immediately to restore services or secure systems. Examples include applying a security patch, resolving a server outage, or addressing a major incident.
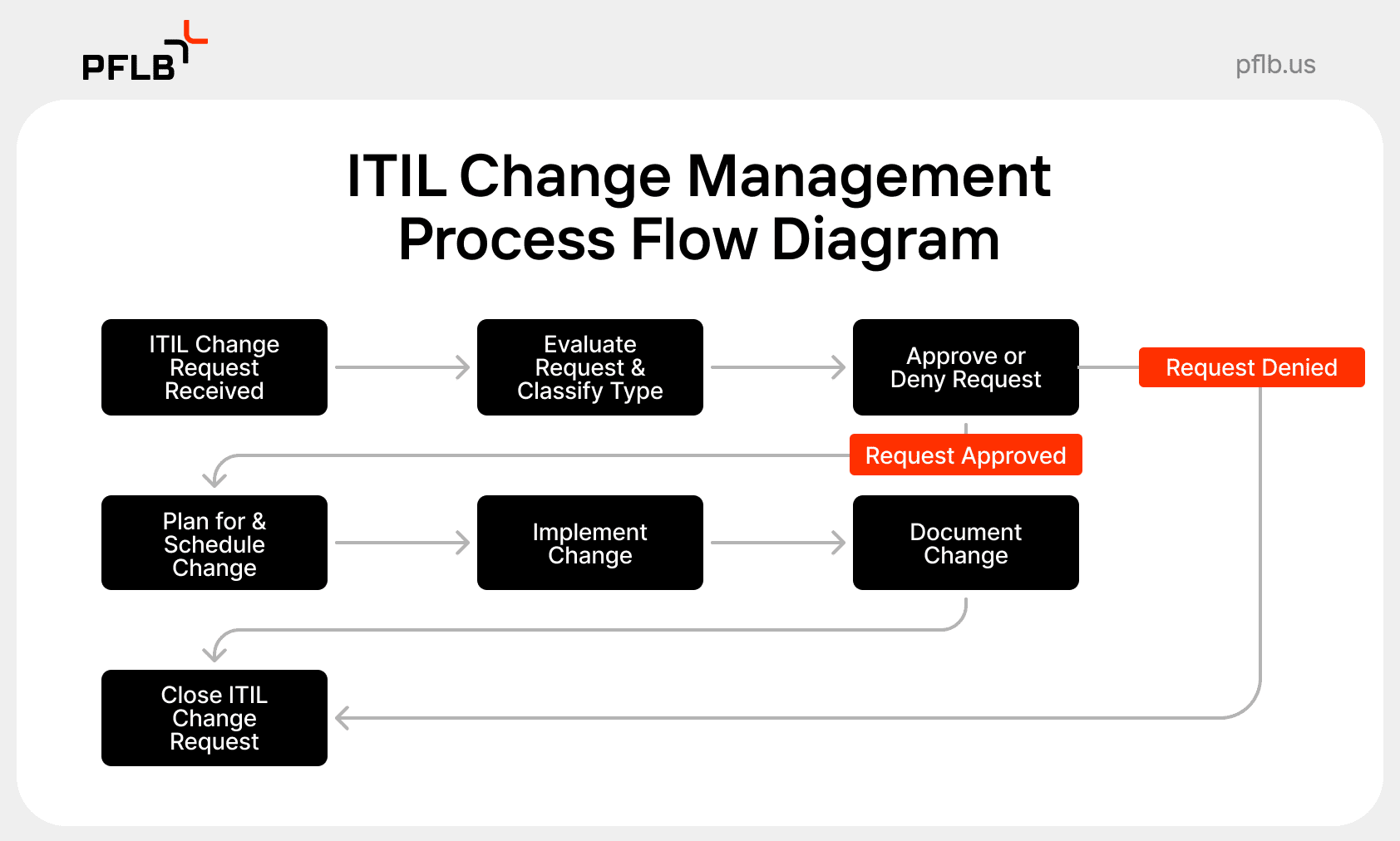
The ITSM Change Management Process
The ITSM change management process involves several key steps designed to ensure that changes are managed effectively from initiation to closure. These steps include initiating a change request, planning and risk assessment, approval process, change implementation, post-implementation review, and closure.
Each step in this process plays a crucial role in minimizing risks and ensuring successful change implementation. By following a structured approach, organizations can better manage changes, reduce service disruptions, and improve overall service quality.
Initiating a Change Request
Initiating a change request begins with the creation of a ticket through a service desk tool, where the necessary details are collected from the outset. The person requesting the change, known as the change requestor, submits a formal Request for Change (RFC). The change manager then reviews, categorizes, and prioritizes incoming requests to determine the next steps.
Documenting the change description, implementation timeline, business justification, and associated risks during the change proposal phase is crucial. This information helps in assessing the feasibility and impact of the proposed change, ensuring that all necessary details are considered before moving forward.
Planning and Risk Assessment
Effective change planning allocates resources appropriately, minimizes downtime, and thoroughly addresses the impact of changes. Key factors evaluated during this phase include feasibility, risk, associated downtime, and potential impact on services.
A thorough risk assessment involves identifying potential risks, costs, and compliance requirements. Understanding an organization’s risk tolerance is key to effective change management planning. By documenting these risks during the change proposal phase, organizations can better prepare for change impacts and minimize disruptions to business operations.
Approval Process
The approval process involves evaluating the proposed change’s impact, cost, benefit, and risk. Relevant authorities, such as the Change Advisory Board (CAB), review and approve the change before implementation. This step ensures thorough consideration of all potential risks and benefits.
Change Implementation
After obtaining necessary approvals, the change implementation phase begins. This phase involves executing the change according to the plan and tracking progress through task assignments and project management tools.
Proper tracking ensures the change is executed as planned and promptly addresses any issues.
Post-Implementation Review
Post-implementation reviews are critical for assessing the effectiveness of the change and identifying areas for improvement. During this phase, the change’s impact is evaluated to determine its overall success and effectiveness.
Feedback from stakeholders is gathered to refine future change processes.
Closure
The final step in the change management process is closure, where the completed change is categorized as successful, failed, or incomplete. This step involves documenting lessons learned and recording all relevant information for future reference.
Regular training and the use of automated ITSM tools can enhance team readiness and engagement in the change management process.
Role of the Change Advisory Board (CAB)
The Change Advisory Board (CAB) plays a vital role in overseeing the evaluation and endorsement of changes within an organization’s IT framework. The CAB is responsible for assessing the risks and consequences associated with proposed changes, ensuring they align with company goals. The CAB maintains a balance between necessary changes and minimizing disruptions by providing recommendations and prioritizing changes, including those reviewed by the emergency change advisory board.
A diverse representation within the CAB, including C-level executives, team managers, technical teams, and finance staff, enhances decision-making by incorporating various perspectives. Change management software helps the CAB document proposals, approvals, and implementation processes efficiently, ensuring smoother service transitions and minimizing disruptions.
Key Metrics for Evaluating Change Management
Monitoring performance is essential for tracking success and ensuring effective outcomes in change management. Key metrics for evaluation include cost per ticket, customer satisfaction, first-contact resolution, schedule variance, unauthorized changes, successful completion percentage, and incident tracking. These metrics offer insights into areas needing improvement, helping organizations refine their practices.
Cost per ticket measures the cost-effectiveness of IT service and support, while customer satisfaction reflects how well the change management process serves user needs. First-contact resolution showcases the effectiveness of support processes, and metrics like schedule variance and unauthorized changes highlight areas where improvements are needed.
Best Practices for ITSM Change Management
Implementing best practices in ITSM change management is crucial for minimizing service disruptions and enhancing service quality. These practices include clear communication, automation with ITSM tools, and continuous improvement.
Clear Communication Plan
Clear communication during ITSM change management helps maintain stability and minimize service disruptions. A communication plan keeps stakeholders informed throughout the change process, reducing inquiries to the service desk. Best practices include providing timely updates, using multiple communication channels, and ensuring messages are easy to understand.
Monitoring the effectiveness of communication ensures information reaches all stakeholders and addresses their concerns. This approach fosters trust and ensures smoother transitions during the change management process.
Automation with ITSM Tools
Standard changes are routine, low-risk, and frequently occur within IT environments. Automating these changes can significantly streamline the approval and deployment processes, minimizing delays and reducing manual errors. Approximately 70% of standard changes can be automated, enhancing overall efficiency and allowing IT teams to focus on more complex tasks.
Automation accelerates the change process and prevents oversight of approval requests. Utilizing ITSM tools for automation ensures that changes are implemented promptly and accurately, contributing to a more reliable IT infrastructure.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a cornerstone of effective change management. Post-implementation reviews assess the effectiveness of changes and identify opportunities for improvement. This process involves evaluating success, analyzing metrics, and gathering stakeholder feedback.
Insights garnered from feedback during the closure phase can be applied to future change initiatives, ensuring ongoing improvement in change management practices. Continuous process refinement leads to fewer failed changes and enhanced service quality.
Benefits of Effective ITSM Change Management
The benefits of a solid change management process are manifold. Effective IT change management keeps technology infrastructure up-to-date with minimal impact, improving service quality and reliability. Efficient change management reduces downtime and avoids costly incidents from poorly managed changes.
Additionally, optimizing resource usage through change management practices supports business objectives and enhances service delivery. Continuous skill development enables better utilization of ITSM practices, contributing to organizational success.
Challenges and Solutions in ITSM Change Management
Common challenges in ITSM Change Management include:
Addressing these challenges requires a balanced approach that combines quick action with careful strategizing to maintain service quality.
Organizations can improve change management by utilizing an ITAM solution integrated with help desk software for better organization and quicker implementation. Embracing a collaborative culture, practices, and tools can significantly help teams overcome these challenges and enhance overall change management effectiveness.
Summary
In summary, ITSM Change Management is vital for ensuring successful implementation of changes while minimizing risks and disruptions. By following a structured change management process, aligning changes with business objectives, and adopting best practices, organizations can enhance service quality and reliability. Embracing continuous improvement and leveraging automation tools can further streamline change management efforts, leading to greater organizational success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary objective of ITSM Change Management?
The primary objective of ITSM Change Management is to minimize risk and ensure successful implementation of changes, thereby enhancing service quality and reliability.
What are the different types of changes in ITSM?
The different types of changes in IT Service Management (ITSM) are standard, normal, and emergency changes. Each type serves a specific purpose in managing IT infrastructure efficiently.
How does a Change Advisory Board (CAB) contribute to change management?
A Change Advisory Board (CAB) contributes to change management by evaluating proposed changes and assessing risks to ensure alignment with company goals while minimizing disruptions. This structured approach fosters informed decision-making and enhances overall change success.
What are some key metrics for evaluating change management performance?
To effectively evaluate change management performance, focus on key metrics such as customer satisfaction, successful completion percentage, and cost per ticket. These metrics provide valuable insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of change initiatives.
What are some best practices for ITSM Change Management?
Implementing clear communication, utilizing automation with ITSM tools, and focusing on continuous improvement are essential best practices for effective ITSM Change Management. These strategies enhance service quality while minimizing disruptions.